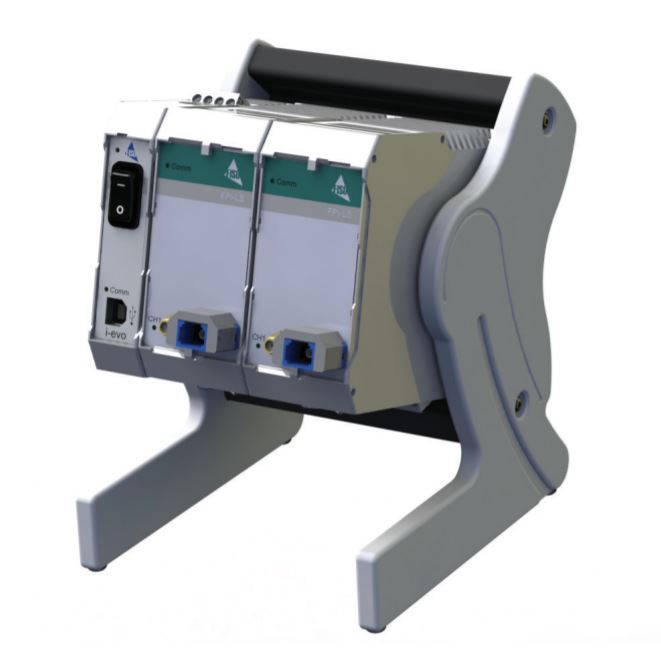
Fiber Optic Micro-Catheter Pressure Transducers (FISO-LS Series)
The “All-In-One” Preclinical Pressure Test Solution for Life Science Research
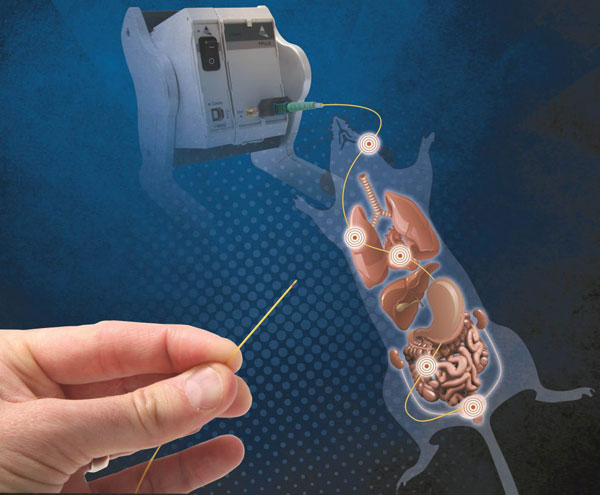
The FISO Catheter (FISO-LS Series) is the ideal pre-clinical solution for small animal physiological pressure testing. Manufactured in Canada by FISO Technologies, SDR Scientific is the authorised distributor for Australia and New Zealand.
The FISO Catheter embodies all the benefits of fiber optics. With a size catheter tip as small as 0.9 French (310 µm), high precision Fiber-Optic sensor and unique MRI compatibility, the FISO Catheter serves as a high precision measurement system designed specifically for physiological research in small animals.
FISO’s catheter has unrivalled ease of use and offers significant advantages over traditional solid-state catheters, while maintaining an excellent performance in signal integrity and frequency response. Optical sensors and fibers are mass-produced, thereby reducing costs and lead times to the research lab.
The complete FISO solution comprises of the:
- FISO catheter
- Signal conditioner in house power supply housing (FPI-LS with EVO Chassis)
- Control and Acquisition software
- Optional extension cables and data acquisition system
- Computer interface and data analysis software (normally supplied by the researcher)
Applications Include:
- Neuroscience—Measurement of Intracranial pressure due to injury, stroke, trauma
- Cardiovascular—Left ventricular pressure; arterial blood pressure. There is minimized impact on blood flow in cardiovascular applications due to sheathing size as small as 0.5Fr.
- Ocular Tonometry—Non-invasive tonometry, glaucoma research in mice
- Urology—Bladder/ureter pressure
- Spine—Intradiscal pressure
- Bone—Intramedullary pressure
- MRI Gating—Arterial blood pressure or Left ventricular pressure for image gating
- Respiratory Physiology
- Gastroenterology
- Otolaryngology
What are the Key Features & Benefits
- Micro – The FISO Catheter combines a miniature (as small as 0.9 Fr or 310 µm) optical pressure sensor at the distal end of the catheter with a fiber optic connector at the proximal end.
- Cost Benefits: Multiple-use catheter and offer significant savings to the researcher. Mass manufacture of optical sensors makes it affordable and obviates the need for expensive solid-state pressure catheters. Re-use of transgenic mice and rats owing to femoral insertion capability with the 0.9Fr model.
- Low noise – Since a beam of light is inherently quiet, no EMI/RF from the catheter itself are interfering with the pressure signal. Plus, it isn’t influenced by high EMI/RF environments. The sensors can be made long enough to be used for MRI image gating.
- Accurate –The FISO-LS conditioner ensures high fidelity pressure traces. Accurate measurements while the animal is inside an MRI machine as the fiber optics technology is immune to interference from RF and EMI.
- No signal artefact – Forward-facing pressure readings at the exact location of interest. This eliminates side-facing sensor measurement artefacts that are commonly encountered by sensor proximity to blood vessel or cardiac wall.
- Proven –This is a proven sensing technology and the pressure transducer has been used in numerous medical and research pressure sensing applications for over 15 years. There are over 1,000,000 sensors in the field.
The unique forward- facing sensing design with the sensor located at the tip of the fiber allows for pressure readings to be taken at the precise location of interest, without any measurement artefacts.
Links to source webpages
Links to any references, papers
Kim, H., Yu, T., Cam-Etoz, B., van Groen, T., Hubbard, W. J., & Chaudry, I. H. (2016). Treatment of traumatic brain injury with 17α-ethinylestradiol-3-sulfate in a rat model, Journal of Neurosurgery JNS, 127(1), 23-31.
Chiba, H., Seo, Y., Sai, S. et al. Renoprotective effects of tolvaptan in hypertensive heart failure rats depend on renal decongestion. Hypertens Res 42, 319–328 (2019).
- Ahmed, J. Ma, I. Rigas, N. Hafezi-Moghadam, E. Iliaki, E.S. Gragoudas, J.W. Miller, A.P. Adamis; Non-Invasive Tonometry in the Mouse. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2003;44(13):3336. doi:
Komuro, K., Seo, Y., Yamamoto, M. et al. Assessment of renal perfusion impairment in a rat model of acute renal congestion using contrast-enhanced ultrasonography. Heart Vessels 33, 434–440 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-017-1063-7